Land cover changes resulting from urban sprawl, transportation network densification, and agricultural practices lead the destruction and fragmentation of wildlife habitats, which can put the survival of animal and vegetal populations at risk. Considering spatial ecological networks and their connectivity in spatial planning and land use management is therefore crucial for preserving biodiversity. In this context, modelling ecological networks is critical to assess their connectivity, propose and prioritize conservation measures (for instance ecological restoration), and compare the impact of prospective development scenarios. This spatial modelling approach complements in highly practical ways other field-based surveys and analyses commonly implemented in ecology.
Graphab is a software program devoted to the modelling of habitat networks using graph-theoretical appraoches. It is the only tool of its kind combining theconstruction and visualization of graphs, with subsequent connectivity analyses and links with external geographical or biological data. It is easily compatible with Geographical Information Systems.
Features

Constructing graphs
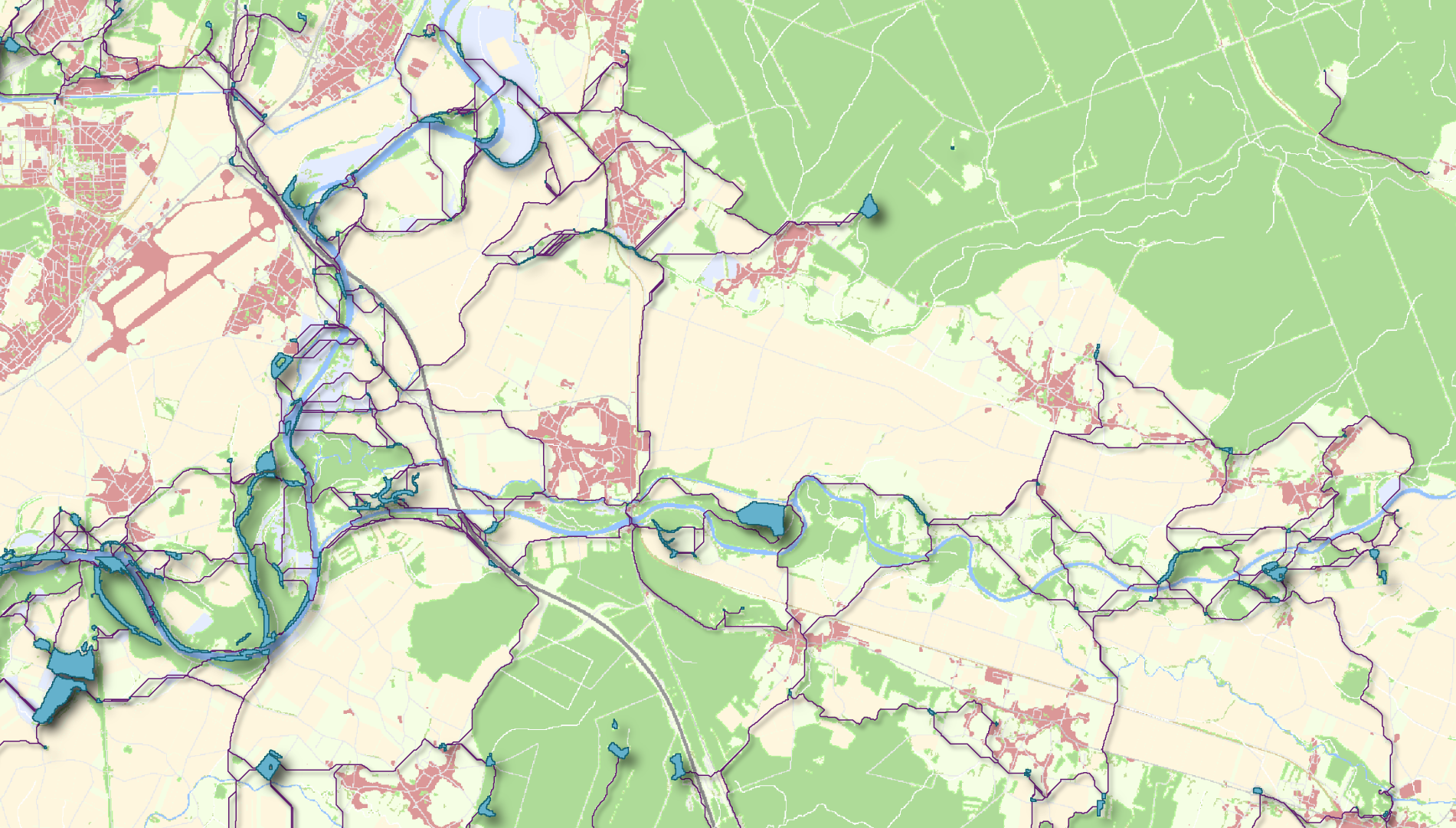

Computing metrics
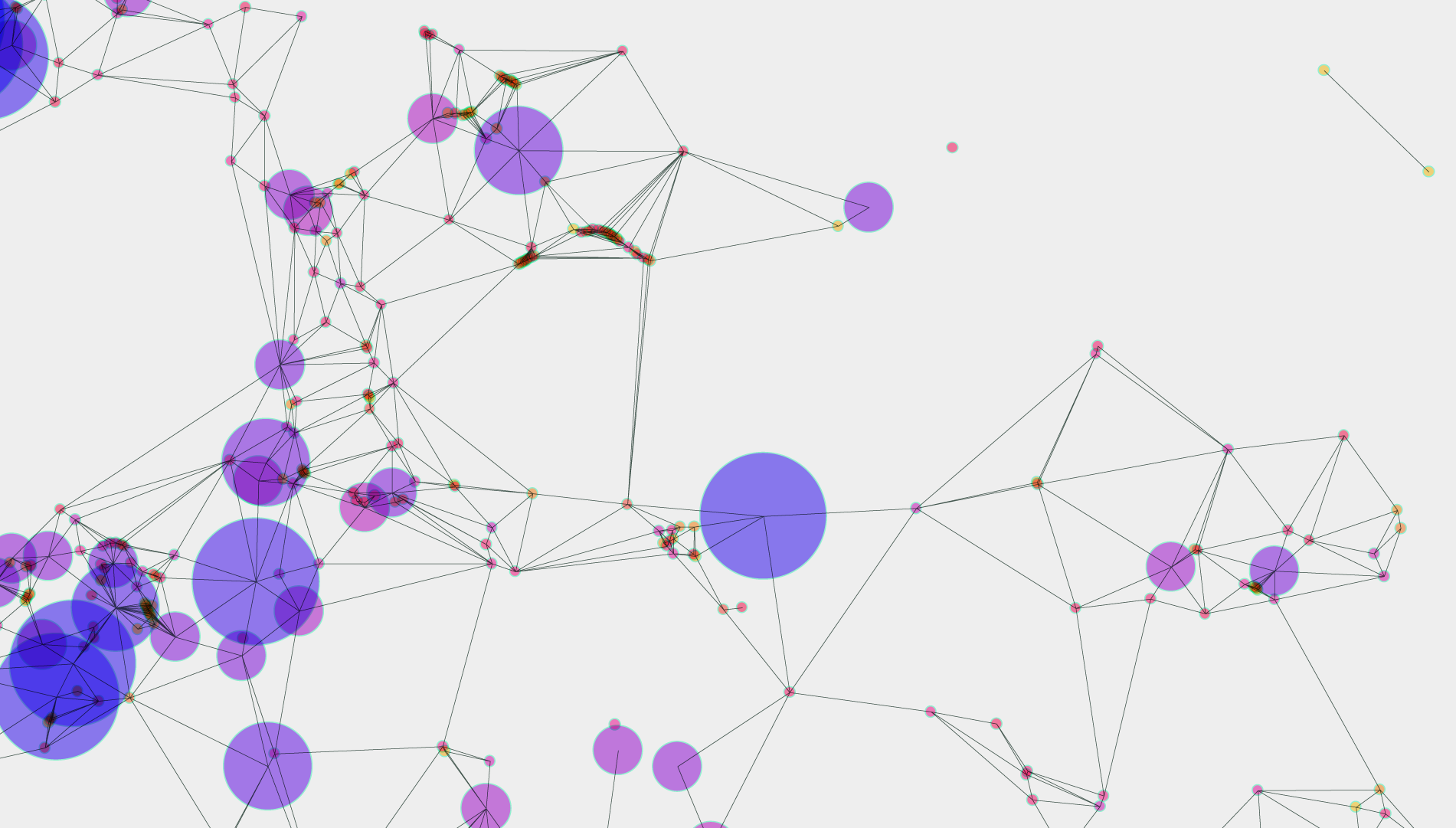

Analysis et generalization
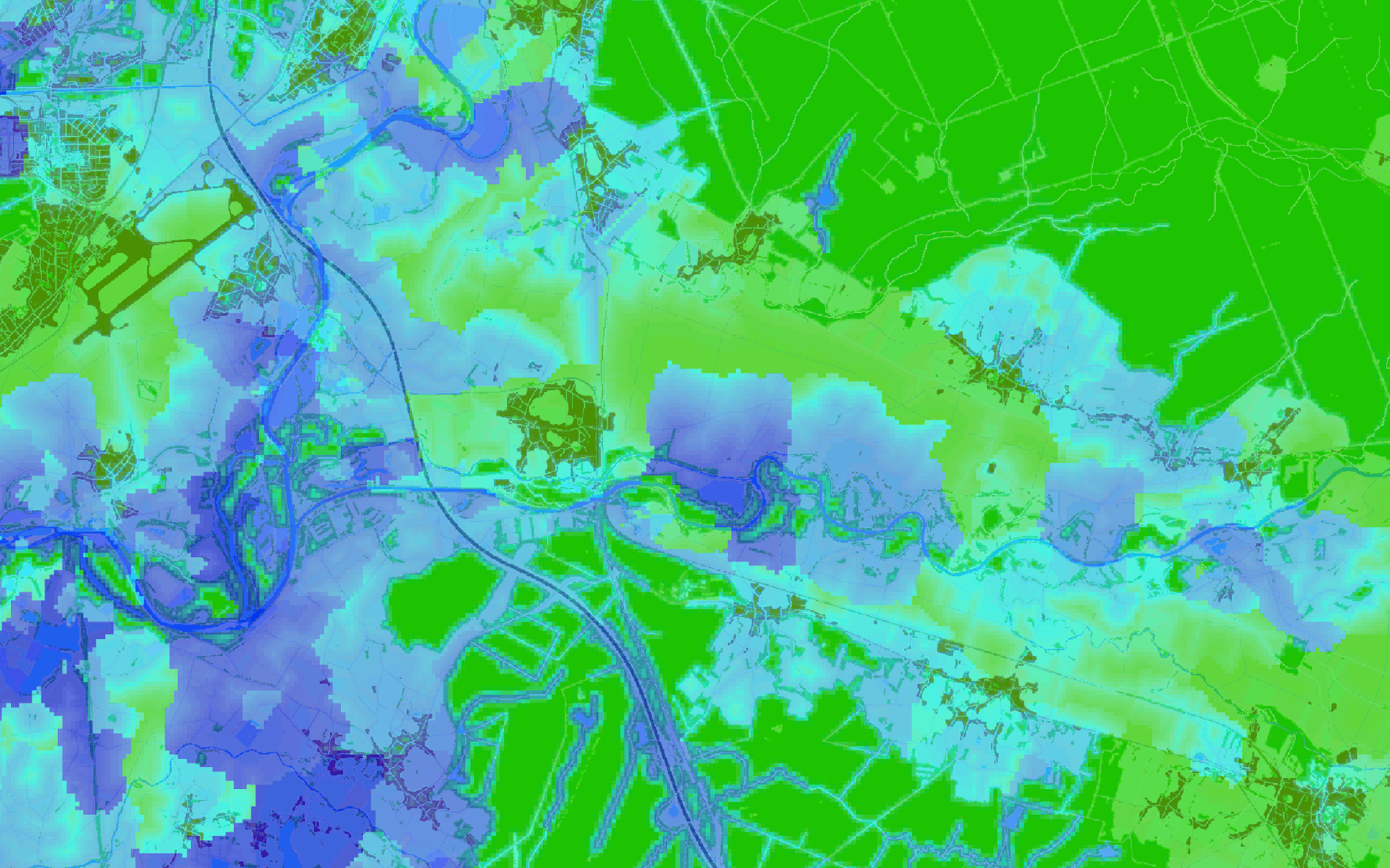
News
Graphab 3.0 is now available!
The last release of Graphab is now available online. The last major changes make it possible to consider multiple habitat types in the same project.
Please note! Projects created with previous Graphab versions are not compatible with this new version.
Forum
The Graphab forum is back online:
Forum Graphab.
Feel free to post your questions!
Download


Graphab runs on any computer supporting Java 11 or later (PC under Linux, Windows, Mac...). It is distributed free of charge.
Graphab is open source and distributed under GPL licence, with the only condition of citing the software :
, 2021. Graphab: an application for modeling and managing ecological habitat networks Software Impacts, 8: 100065.
, 2012. A software tool dedicated to the modelling of landscape networks Environmental Modelling & Software, 38: 316-327.










